This guide teaches developers how to set up their workstations in order to use Samsung Mobile SDKs in their apps. It covers basic topics such as how to download and install the SDK.
The Visual Studio Emulator for Android simplifies this by introducing Device Profiles. We’ve curated a set of device profiles that represent the most popular hardware in the market, including devices from Samsung, Motorola, Sony, LG, and more. In Visual Studio 2015 RC, you’ll find a new option in Visual Studio under the Tools menu–a link. Mar 23, 2015 Fill out your device list and let everyone know which phones you have! Edit Your Device Inventory. Introducing XDA Computing: Discussion zones for Hardware, Software, and more! Q Hardware Profile for Android Studio. Thread starter loadedmind. Start date Mar 23, 2015.
This section covers:
- System Requirements.
- Downloading Samsung Mobile SDKs.
- Getting started with Android Studio.
1. System Requirements
To develop apps for Samsung mobile devices, you must first set up your Android development environment. If your development environment is already configured, you can skip this section.
- Verify that your development system meets the requirements specified by the Android System Requirements.
- Set up your Java environment:
To develop Android apps in Java, you need the following:
- Java Development Kit (JDK) — this provides the tools required to build a Java app.
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE) — this lets you run Java apps on your computer.
To set up these components:1. Go to Java SE Downloads.2. Click Java Download to display the download page for the latest version of JDK, which includes JRE.3. Click the download package for your operating system: Windows, Mac OS X, or Linux.4. Install the JDK package. For details about the installation, see the Java Platform Installation.
- Download Android Studio:
- Go to Android Studio.
- If the browser has detected your operating system, click Download Android Studio. Otherwise, click Download Options and select a different platform: Windows, Mac OS X, or Linux.
- Unzip and install the bundle. It includes essential components and the Studio IDE.
- Launch Android Studio.
- If you get a notice of Platform and Plugin Updates, click update to exit Studio and launch the SDK Manager. Then install the suggested packages.
2. Downloading Samsung SDKs
Downloading SDKs from Samsung Developers:
- Go to Mobile page
- Select the SDK you want to download
- Go to the Resources page for the SDK
- Click the download button
- Read the license agreement, select I agree to this SDK License Agreement and click Download
- Unzip the downloaded SDK to a folder of your choice. The SDKs typically provide the following folders
- Docs: Programming guides and API references
- Libs: Java and C libraries to use in your app
- Samples: Sample apps showing example source code
- Tools: Additional tools that may be needed to use the SDK
- Extras: Additional support resources
3. Getting started with Android Studio
This section describes how to create your first project in Android Studio and run an app.
Creating an Android Studio project
- Launch Android Studio.
- Create a new project by clicking File > New Project
- Fill out the fields:
- Application name: your app name
- Company domain: the qualifier for your app package name.
- Package name: this is the combination of the company domain and application name, which must be unique across all packages in the Android environment. Android generates this from the application name and company domain values.
- Project Location: the directory where your app is stored. You can use the default or specify another location, if desired.
- Click Next
- Select the type of device you want to target, for example, Phone and Tablet
- Select the Minimum SDK level you need to support the SDKs you’re using. In this example, select API 21. Click Next
- Use the default Empty Activity type and click Next. For more about activities, see Android Activities.
- Use the default Activity Name and Layout Name and click FinishFor more about creating a project in Android Studio, see Creating Projects.
Adding a Samsung library to Android Studio
To use a Samsung SDK in your app, you add the library files that are bundled with the SDK to your Android Studio project.
- Open your project in Android Studio.
- Use a file browser to navigate to the folder containing the Samsung SDK
- Open the add-on SDK folder, then open:
- Docs > API Reference > index.html: to see what libraries and API methods are provided by the SDK
- Libs folder: to copy the libraries you want to use in your app
- In your Android Studio project, top-left drop-down menu, change the Android view to Project
- Right-click your app’s libs directory and select Paste
- In the Copy dialog, click OK to paste the copied files into your project
- The libraries now appear in your project under the libs folder
- Right-click the libraries and select Add As Library.
- Select the module to add the library to. If your app contains several modules, ensure that you add the library to the appropriate module. Click OK.Your project now includes the SDK you downloaded.

Running the App
Android Studio provides two ways to compile and test your app:- On an Android Virtual Device (AVD)- On a physical Samsung deviceTo run your app:
- Plug your Samsung mobile device into your computer using a USB cable
- If you are using a Windows computer, go to Samsung Android USB Driver for Windows, then download and install the USB driver onto your computer
- Enable developer options on your device by going to Settings > About device > Software info and tapping Build number seven times. (Devices with Android 4.1 or older already have developer options displayed by default.)
- Turn on USB debugging by tapping Settings > Developer options > USB debugging
If My Knox is installed, USB debugging is grayed out; try using another device.
- In Android Studio, with your project open, click Run > Run 'app' (or press Shift + F10)
- Select the device you want run the app on, under either Connected Devices or Available Emulators
Running a sample app
The sample apps are in the Samples folder of the SDK you downloaded.To run a sample app:
- Open Android Studio
- In the top navigation menu, select File > Open
- Navigate to the sample app directory in the SDK you downloaded
- Click OK to import the file to your project
Hardware Profiles For Android Studio Free
Abstract
Developers have been using the Intel® Hardware Accelerated Execution Manager (Intel® HAXM) based Android* emulator for developing Android* apps, but it had a limitation when it came to testing apps that use Google APIs. The x86 based Google APIs system image was added to Android SDK recently. In this article we look at how to install, configure and test the HAXM based emulator with Google APIs. We will create a sample app to demonstrate how you can use the Google APIs and test them with the HAXM based emulator.
Contents
Overview
The Intel HAXM Android emulator is extremely fast as it uses hardware accelerated virtualization. Developers can see great productivity gains in their Develop-Debug-Test cycle of app development. Until recently we were not able to test Android apps that use Google APIs, as there were no x86 based Google APIs emulator images.
We now have standard x86 Google API emulator images available in Android SDK. The article below on the Intel Developer Zone goes into more detail about how to setup and create an AVD configuration for running x86 Google API image.
There were some issues reported in the comments section. On some systems if you enable “Use Host GPU” checkbox for the emulator image, some Google apps (e.g. Maps) that use OpenGL related technologies seem to crash. Disabling the GPU emulation may fix the issue.
Install The Latest x86 based Google APIs Image
An updated bug fix version (v5) for the image has been released recently. Select and install the image as shown below.
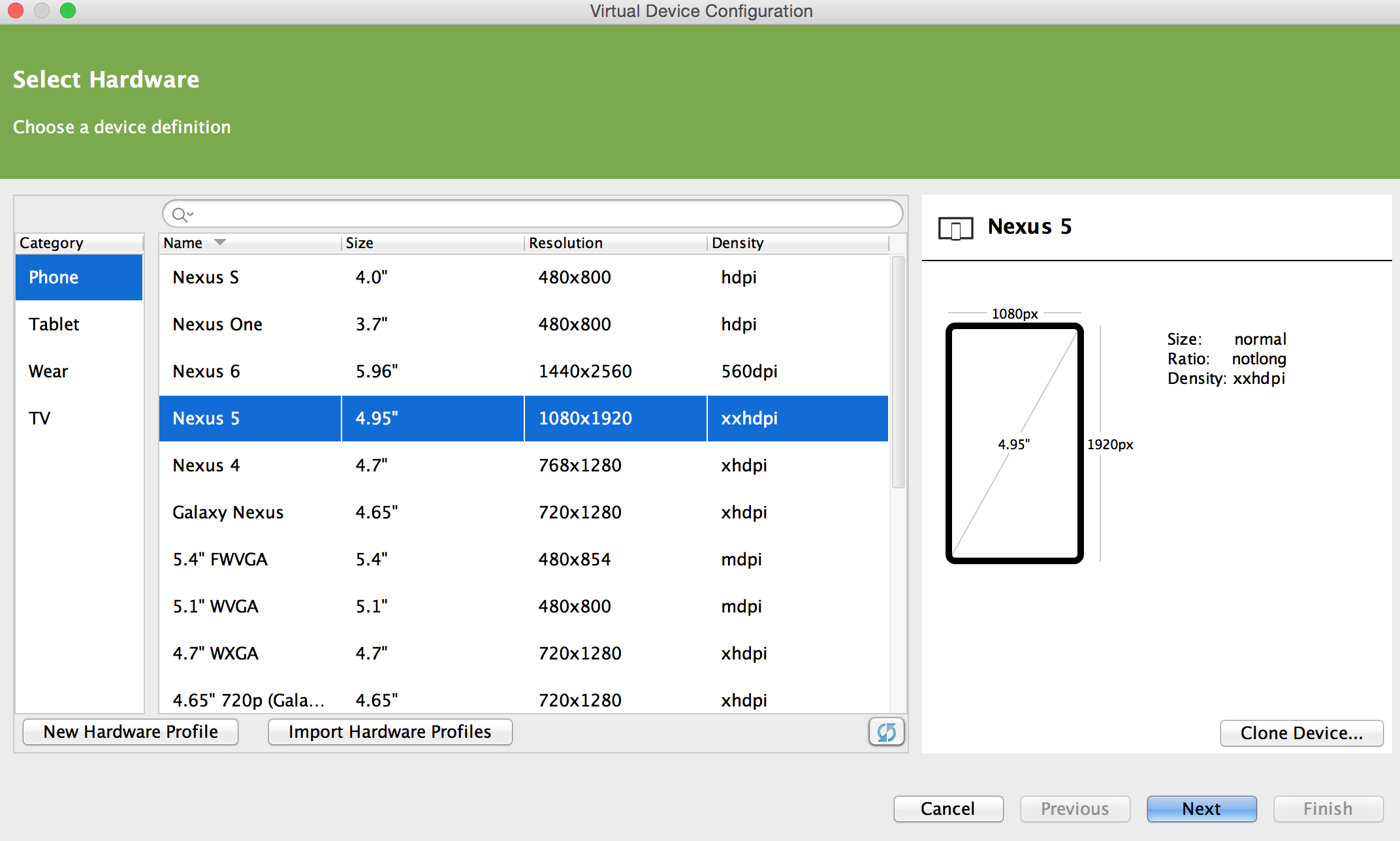
Figure 1: Google APIs x86 Image in Android SDK
Create Android Virtual Device (AVD) Configuration and Test
Create an Android Virtual Device configuration for your target device profile of choice. The following screenshot shows the AVD configuration for Nexus 4 profile. Please note the “Target” option showing the x86 System with Google APIs with API level 19.
Figure 2: Selecting the correct target for AVD configuration
Start the emulator image, the “Starting Android Emulator” window will show the message “HAX is working and emulator runs in fast mode”, if HAXM is being used successfully.
Figure 3: Shows HAXM is being used successfully
Once the Android emulator image is booted, the apps screen should show some standard Google apps like Maps and Google Settings. Please refer to the following screenshot.
Figure 4: Google APIs x86 Image with Google Apps
Click on Google Maps to verify that your HAXM based x86 Google APIs image is working properly.
If you do not see the Maps displaying properly, check to see if your emulator has network connectivity by opening the browser app and testing your favorite website. By default, the emulator should automatically get network access and internet connectivity (if your host system has it). Using proxy configuration on a host system can sometimes cause network related issues in emulator.
Resolve all the network issues, and verify your android emulator can connect to the internet.
The following screenshot shows the Google Maps app running inside the Intel HAXM based Android emulator. It uses the AVD configuration (x86_19g) we created earlier.
Figure 5: Google Maps App running inside x86 Google APIs image
Install Google Play Services SDK
Before we can use Google APIs in our Android app, we first need to download Google Play Services SDK in Android SDK Manager.
The below article goes into detailed setup instructions.
Below is a screenshot of Android SDK Manager showing Google Play Services selected for installation. It is listed under the “Extras” section.
Figure 6: Install the Google Play Services using Android SDK Manager
At a higher level, Google APIs on Android depend on two main components:
- The Google Play Services, which runs as a background system service on the Android OS. It is automatically updated by Google Play Store just like any other APK.
- Client Library, which is a thin API wrapper with a consistent interface. This is part of the Google Play Services SDK we downloaded earlier. Developers need to make sure they use the latest, correct version in their apps.
The following article goes into more detail on how these 2 pieces work together to provide seamless access to Google APIs for Android Apps.
Create a Sample App To Test Google APIs in x86 based Emulator
Next, we will create a basic app to try out Google APIs with x86 Android Emulator Image under HAXM.
Android Studio is used for creating the sample app. Click on File -> New Project to create a basic app with a single main activity. As our x86 Google API image is using API level 19, make sure to use the same one for Compile and Target options. The following screenshot shows all the options chosen for our sample app.
Figure 7: Creating a default app in Android Studio with correct API levels for x86 Google API image
Go ahead and build the app, and run it inside the emulator AVD configuration (x86_19g) we created earlier. By default, the app should display a 'hello world” message.
We will now add Google Play service Client library to our app. It is easier with an Android Studio project; we just need to modify the build.gradle file under our app module (not the main project’s build.gradle). Simply add the reference to the latest google play services under the dependencies, highlighted in the following code snippet.

Code Snippet 1 ++
The reference documentation goes into more detail: http://developer.android.com/google/play-services/setup.html
Google Play Services and Client Library provide access to several Google APIs – Maps, Drive, Location, Google+, Ads among others.
For our sample test app, we will use the Google Maps Android APIs. We need an API key to access the Google Maps Android API. Please follow the instructions in the following reference article to create your API key: https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/android/start#obtain_a_google_maps_api_key
Once you have obtained the API key, modify the App manifest to add your API key, replace the text (<ADD YOUR KEY>) highlighted in green with your API key.
We have a few other additions to the app manifest: Google Play Service version, and depending on APIs used, the required permissions.
For Google Maps, we need internet, network_state, and external_storage at a minimum. Please refer to https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/android/start#specify_app_settings_in_the_application_manifest for a detailed explanation.
The following code snippet shows the entire app manifest file used for our test sample app.
Code Snippet 2 ++
We should now be able access Google APIs and invoke Google Map objects.
For a simple Google Maps invocation we can just use the MapFragment and replace our “hello world” layout with it. Modify the contents of the default “activity_main.xml” with the following code snippet, as mentioned in https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/android/start#add_a_map
Code Snippet 3 ++
Rebuild the app, and run it on the emulator. Instead of the “hello world” message, we should now see the entire space occupied by the MapFragment displaying basic google maps with default controls.
Figure 8: Google maps API working and tested with HAXM based Android emulator using sample app
Users can drag the map around and click on zoom controls to interact with the map, just like on a real device. It provides a smooth experience with no noticeable artifacts, latencies or delays.
Summary
This article discussed installation, configuration and setup of x86 based Google APIs system image on the Intel HAXM based Android Emulator. We also discussed how to setup Google Play service SDK and created a basic app to test accessing of the Google APIs from the Emulator.
About the Author
Ashok Emani is a Software Engineer in the Intel Software and Services Group. He currently works on the Intel® Atom™ processor scale enabling projects.
| Optimization Notice |
|---|
| Intel's compilers may or may not optimize to the same degree for non-Intel microprocessors for optimizations that are not unique to Intel microprocessors. These optimizations include SSE2, SSE3, and SSE3 instruction sets and other optimizations. Intel does not guarantee the availability, functionality, or effectiveness of any optimization on microprocessors not manufactured by Intel. |
| Microprocessor-dependent optimizations in this product are intended for use with Intel microprocessors. Certain optimizations not specific to Intel microarchitecture are reserved for Intel microprocessors. Please refer to the applicable product User and Reference Guides for more information regarding the specific instruction sets covered by this notice. |
| Notice revision #20110804 |
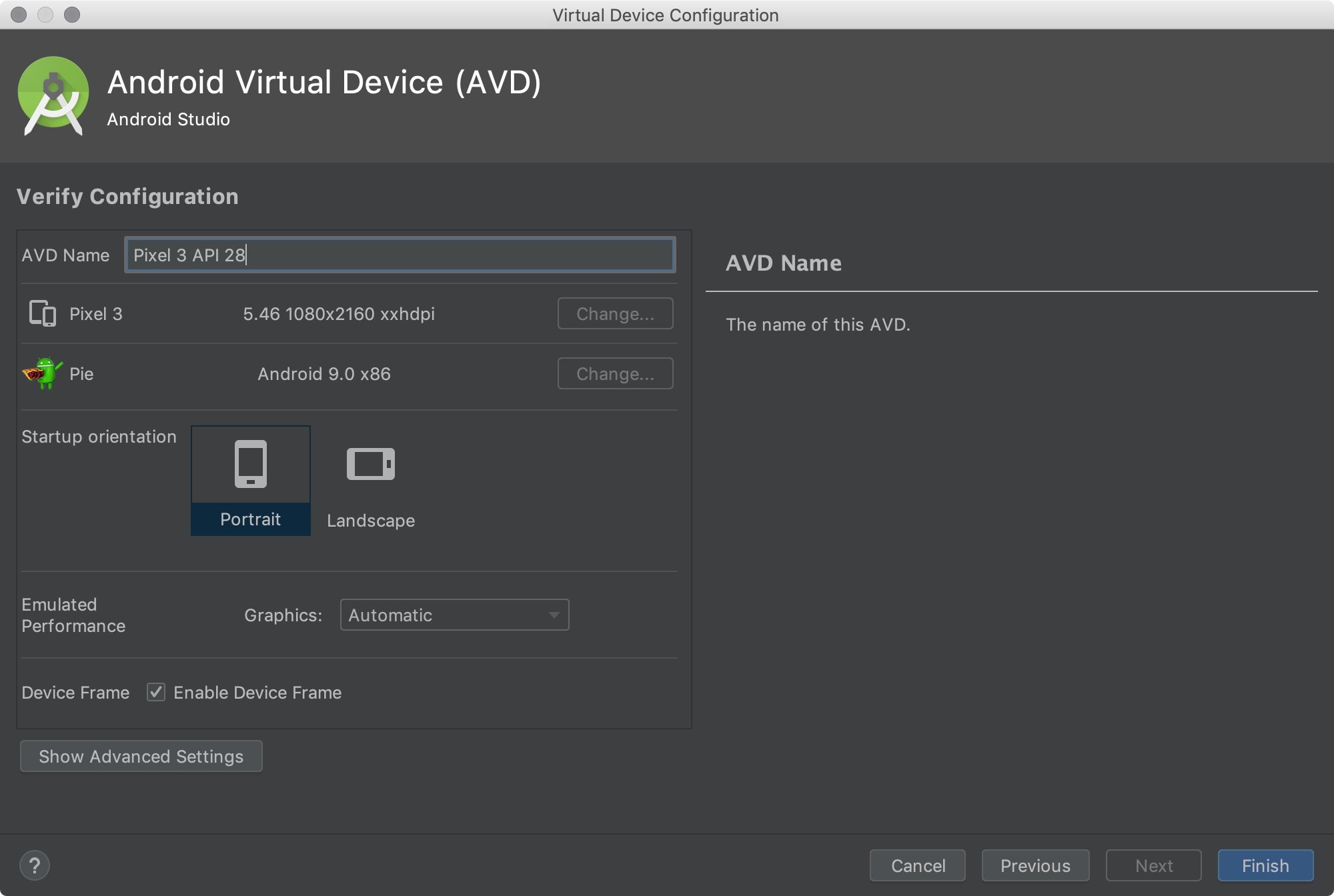
Other Hardware Profiles For Android Studio
++This sample source code is released under the Intel OBL Sample Source Code License (MS-LPL Compatible)